

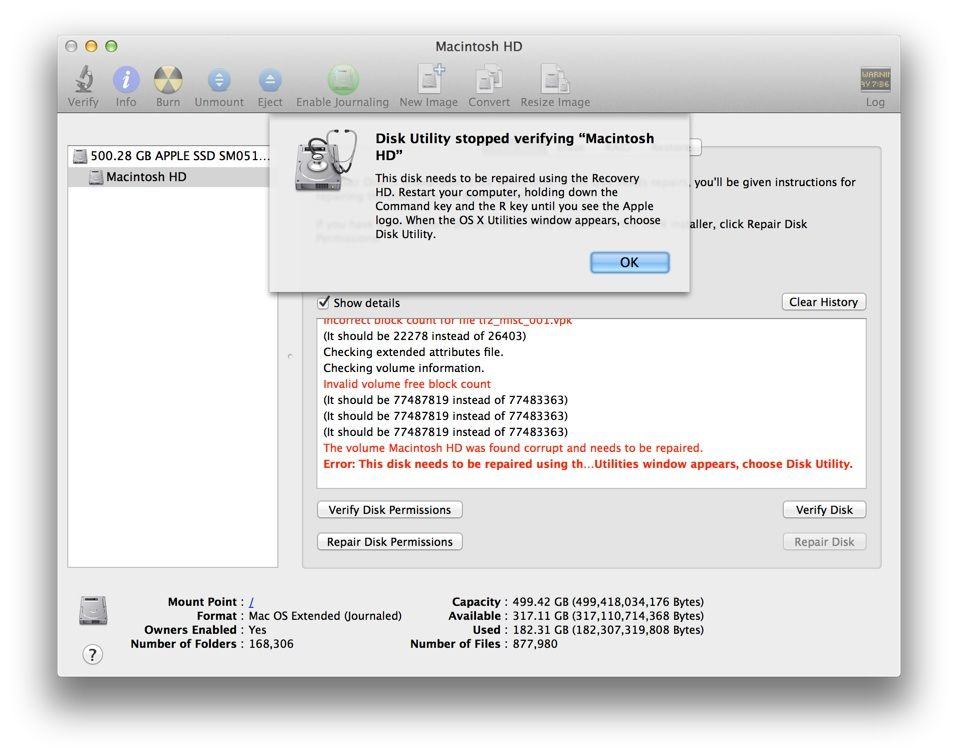
In order to get the partition associated with this UUID, you can use the use the “blkid” command in the following way. If you are not mounting the root device, you should set this option to “2” or “0” as “1” is reserved for the root device.Īs you can see here, besides mounting the “ sda1” partition in the previous section, only the partition with the UUID shown above would be mounted.

Options : some options that you can specify in order to tune your mount (“ro” for a read-only mount or “noexec” to prevent binary execution).Filesystem type : the type of filesystem you use to format your disk.Mountpoint : the directory on the filesystem that you are going to use in order to access data stored on the disk.Filesystem : you can either specify a UUID (for universal unique identifier), a label (if you chose a label for your disk), a network ID or a device name (which is not recommended at all).UUID=b9df59e6-c806 / ext4 errors=remount-ro 0 1 # that works even if disks are added and removed. # device this may be used with UUID= as a more robust way to name devices # Use 'blkid' to print the universally unique identifier for a # /etc/fstab: static file system information. To list permanent mounted partitions on Linux, use the “ cat” command on the fstab file located in /etc. The “ fstab” file is a very important file on your filesystem.įstab stores static information about filesystems, mountpoints and several options that you may want to configure. If you were to reboot your system without adding your mount settings to the “fstab” file, your drive partition would not be mounted on reboot. Using the “mount” command does not make your mounts permanent : you need to add them to the fstab file for them to be permanent. Your drive partition was correctly mounted on the mountpoint, however there is one little gotcha that you need to be aware about when mounting drives. In order to check that your drive partition was correctly mounted, you can use the “lsblk” and inspect the mountpoint column. If you did not get any error messages in the process, it means that your drive partition was successfully mounted! Check Mounted Drives on Linux To mount the “sda1” partition, use the “mount” command and specify the directory where you want it to be mounted (in this case, in a directory named “mountpoint” in the home directory. In this case, we want to mount the “ sda1” partition on our filesystem. Unfortunately, this command does not list the current mountpoints used by your drives. ├─sdb1 ext4 b9df59e6-c806-4851-befa-12402bca5828 /Īlternatively, you can use the “ blkid” command in order to locate and list block devices on your system. To list partitions with filesystems types, use the “lsblk” command with the “-f” option. In order to mount drives on Linux, you have to use the “ mount” command using the following syntax $ sudo mount įirst of all, you need to check the disk partitions already created on your system that are not already mounted.
#Mac unmount disk how to
If you are not sure how to give sudo rights to users on Debian/Ubuntu or CentOS/RHEL, make sure to check our dedicated guides on the subject. User may run the following commands on schkn-ubuntu: To verify that you have sudo privileges, you can run the “ sudo” command with the “ -l” in order to list the privileges you currently own. In order to mount drives and filesystems on Linux, you need to have sudo privileges on your machine. Unmounting drives on Linux using umount.Mounting Drives Permanently using fstab.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
